Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a machine that measures and record electrical activity of the heart. ECG is used to diagnose and monitor many heart conditions ranging from electrical conduction problems (AV node and bundle branch blocks) through rhythm issues (Arrhythmias) to cardiac muscle diseases like ventricular hypertrophy and myocardial infarction among others.
ECG interpretation is only possible and reliable if the connection of electrodes and recording is done correctly. 10 electrodes are needed to record a 12 lead ECG.
Definition of terms
ECG Electrodes are small sticky electrically conductive metals that are placed on the patient’s body at different locations to record Electrical signal coming from the heart. They are usually coated with conductive gel to increase sensitivity and decrease discomfort on the patient. In the past reusable electrodes were used but in most places today, disposable electrodes are preferred to prevent infection spread and maintenance of hygiene.

ECG Leads are recordings of an electrical activity of the heart on an electrocardiograph. To get a 12 lead ECG you need 10 electrodes placed on the chest and limbs of the patient connected by wires to an ECG machine.
Electrocardiograph is a graphic representation of electrical activity of the heart on various leads.
Labelling
The ten electrodes are labelled as follows:
- RA for right arm, usually has red color code
- LA for left arm with yellow color code
- LL for left leg with green color
- RL for right leg with black color.
- V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6 which all are connected on the chest
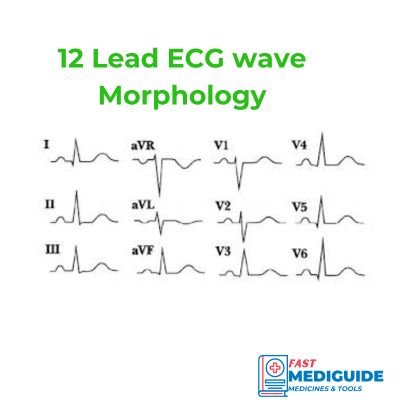
The twelve leads that are used to interpret ECG are divided into two main groups:
- Six Limb leads that process electrical signal from the all 4 limb electrodes labelled as Lead I, II, III, aVR, aVL, and aVF.
- Six precordial leads that process electrical signal of the heart from the chest electrodes. They are labelled as V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6.
The image below is an example of an ECG showing the twelve leads and morphology of the waves.
Preparations Before Recording ECG
Ensure the patient is lying in supine position and explain the procedure. Bed can be inclined if the patient has orthopnea or discomfort when lying supine. ECG recording is painless to the patient.
Patient should also be warm and relaxed to prevent muscle tremor which interferes with ECG recording. Avoid sources of electrical interference such as cell phones, electrical instruments and devices near the patient.
Remove excess hair on the skin where electrodes will be placed to improve conduction.
Finally ensure the skin is clean and dry for stability of the electrodes.
Electrodes Placement
When placing electrodes, you should start with limb electrodes, followed by chest electrodes. In an emergency setting it is easier and quicker to just look at color codes and place the electrode in the correct place than to read the label on each wire manually.
You should generally connect limb electrodes in this order; Right arm (RA), Left arm (LA), Left leg (LL), and Right leg (RL). In terms of colors it should be Red, Yellow, Green, Black, going in clockwise direction.
The mnemonic to remember is “Ride Your Green Bicycle”. R for red, Y for yellow, G for green and B on Bicycle for black or right leg. The following table shows where to place each of the limb electrodes.
| Electrode | Position |
|---|---|
| RA | Right arm just above wrist |
| LA | Left arm just above wrist |
| LL | Left leg medial side between ankle and knee |
| RA | Right leg medial side between ankle and knee |
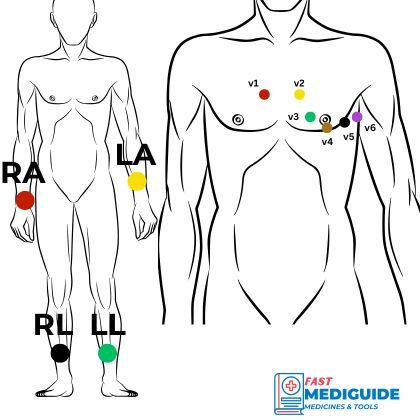
For placement of chest electrodes, you the following order is recommended:
- Place V1 on 4th intercostal space on right sternal border, then
- Place V2 on 4th intercostal space on left sternal border, then
- Place V4 on 5th intercostal space midclavicular line left side (around nipple area), then
- Place V3 midway between V2 and V4, then
- Place V5 on left anterior axillary line same level as V4, finally
- Place V6 on left mid-axillary line same level as V4 and V5
The diagram below illustrates where each electrode is places to explain above concepts.
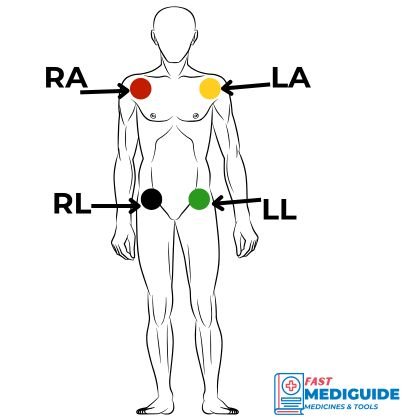
In the case where a person has missing limb or some other condition that prevent you from placing limb electrodes on the limbs you can:
- Place Arms electrodes on the shoulders
- Place leg electrodes on the groin on each side.
ECG Calibration
12 lead ECG should be calibrated to normal standard values in order to interpret it accurately. Make sure the label on calibration states that 10mm is equal to 1mV so that you can convert wave height into a meaningful voltage.
The normal paper speed is set to 25mm per second, which implies that 1mm equals 40milliseconds (0.04s).
ECG can be disconnected at any order after printing or finishing to record, no harm will be done on the patient.
More medical tools and guidelines on our home page.